
The uranium salts caused a blackening of the plate in spite of the plate being wrapped in black paper. All results were negative until he used uranium salts. He wrapped a photographic plate in black paper and placed various phosphorescent salts on it. These materials glow in the dark after exposure to light, and Becquerel suspected that the glow produced in cathode ray tubes by X-rays might be associated with phosphorescence. Radioactivity was discovered in 1896 by scientists Henri Becquerel and Marie Skłodowska-Curie, while working with phosphorescent materials. Pierre and Marie Curie in their Paris laboratory, before 1907 Well-known examples are uranium and thorium, but also included are naturally occurring long-lived radioisotopes, such as potassium-40. These 34 are known as primordial nuclides. There are 28 naturally occurring chemical elements on Earth that are radioactive, consisting of 34 radionuclides (6 elements have 2 different radionuclides) that date before the time of formation of the Solar System. When the number of protons changes, an atom of a different chemical element is created.



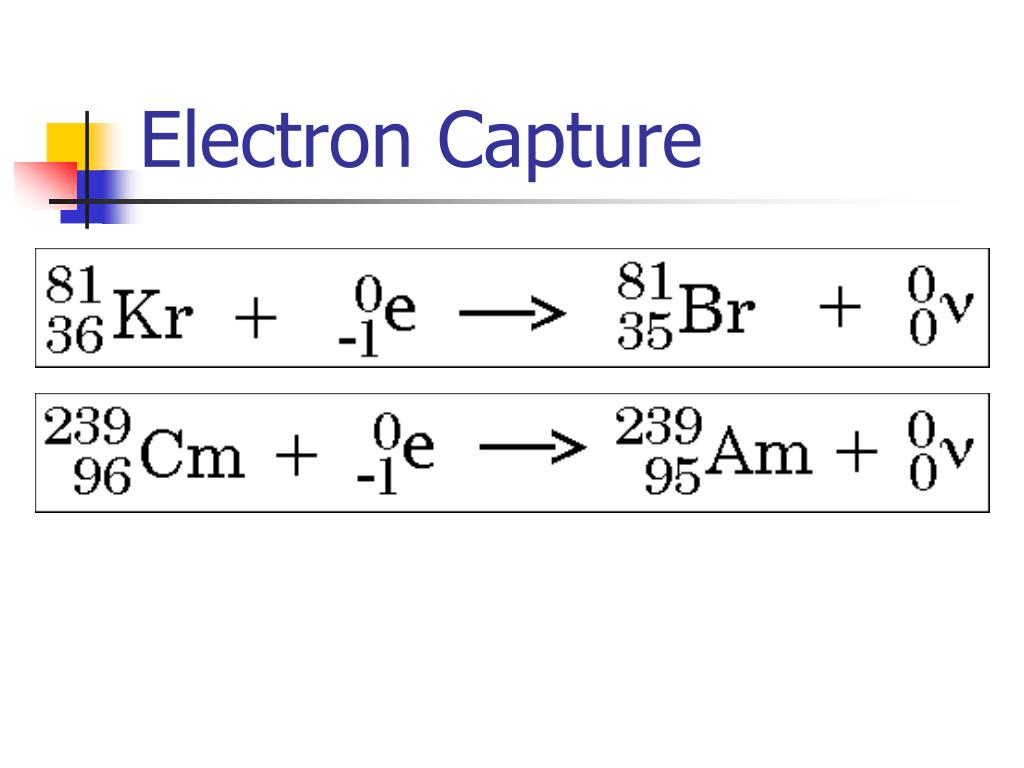
Except for gamma decay or internal conversion from a nuclear excited state, the decay is a nuclear transmutation resulting in a daughter containing a different number of protons or neutrons (or both). The decaying nucleus is called the parent radionuclide (or parent radioisotope ), and the process produces at least one daughter nuclide. The half-lives of radioactive atoms have a huge range from nearly instantaneous to far longer than the age of the universe. However, for a significant number of identical atoms, the overall decay rate can be expressed as a decay constant or as half-life. According to quantum theory, it is impossible to predict when a particular atom will decay, regardless of how long the atom has existed. random) process at the level of single atoms. The weak force is the mechanism that is responsible for beta decay, while the other two are governed by the electromagnetism and nuclear force. Three of the most common types of decay are alpha, beta, and gamma decay, all of which involve emitting particles. A material containing unstable nuclei is considered radioactive. In this process, a positron will be emitted from the nucleus.Radioactive decay (also known as nuclear decay, radioactivity, radioactive disintegration, or nuclear disintegration) is the process by which an unstable atomic nucleus loses energy by radiation. In positron decay, the mass number of an atom doesn’t change, but the atomic number decreases by one. But potassium (K) is converted into argon (Ar) as the atomic number changes by one unit.Įquation electron capture reaction is similar to that of positron decay. The equation for electron capture can be written as, Electron capture reactions are also called K-electron capture or L-electron capture, because electrons are absorbed from the K or L shell of the atom. The energy released during this process comes out as gamma rays. Then the absorbed electron and one proton combines to form a neutron, thereby balancing the number of protons and neutrons in the nucleus. The nucleus absorbs an electron from the K-shell or L-shell of the atom. A nucleus undergoes electron capture, if it contains more number of protons compared to that of neutrons. This process involves emission of high energy gamma rays from the nucleus.Įlectron capture is a nuclear process. A nucleus rich in protons absorbs an inner electron from the atom. Hint: Electron capture is a nuclear process.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
